What are Tannins in Wine?
Tannins in Wine
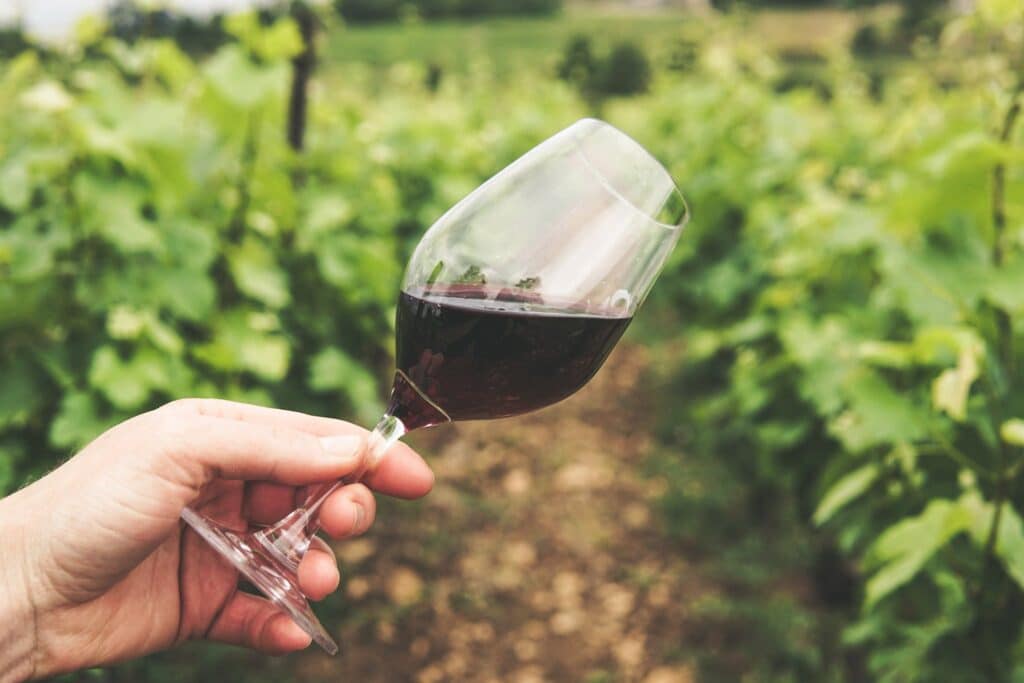
Tannins in wine are phenolic compounds found in grape skins, seeds, and stems. They contribute to the texture, balance, and structure of the wine. Tannins are responsible for the astringency or dry, puckering sensation in the mouth when you drink wine. They play a crucial role in shaping a wine’s overall profile.
What type of wine has the most tannins?
Red wines generally have the most tannins compared to white wines. This is because red wines are made by fermenting the juice with grape skins, seeds, and sometimes stems rich in tannins. Varieties like Cabernet Sauvignon, a Bordeaux What exactly is a Bordeaux? Bordeaux ble... More blend varietal, and Nebbiolo are known for their high tannin content.
What exactly is a Bordeaux? Bordeaux ble... More blend varietal, and Nebbiolo are known for their high tannin content.
How can you detect tannins in wine?
You can detect tannins in wine by the sensation they create in your mouth. When you taste a wine with significant tannins, you’ll feel a dryness and astringency, especially on your gums and the inside of your cheeks. Additionally, the wine may have a slightly bitter or chalky taste.
How do tannins affect the taste of wine?
Tannins can have a profound impact on the taste of wine. They contribute to the wine’s structure and aging potential. In young wines, robust tannins can make the wine taste firm, astringent, and somewhat bitter. However, tannins soften and integrate as wine ages, contributing to a smoother and more complex flavor profile.
What are the benefits of wine tannins?
The benefits of wine tannins include improving a wine’s aging potential, adding complexity and depth to its flavor, and enhancing its ability to pair with food. Tannins can also provide a pleasant, tactile sensation in the mouth that many wine enthusiasts appreciate.
FAQs:
How do you soften tannins in wine?
To soften the tannins in wine, you can allow the wine to age, which will naturally mellow the tannins over time. Decanting wine or using aerators can also help by exposing it to oxygen, which can help soften the tannic structure. Pairing wine with foods that have fat or protein can mitigate the perception of tannins in your mouth, making the wine taste smoother.
What are the positive effects of wine tannins?
Positive effects of wine tannins include enhancing a wine’s aging potential, adding structure and complexity, and aiding in food pairing. However, excessive tannins in a young wine can make it less approachable.
Are there adverse effects of wine tannins?
Adverse effects of wine tannins primarily occur when they are too harsh or unbalanced, leading to an unpleasant, overly astringent taste that can overwhelm the other flavors in the wine. This can result from poor winemaking practices or underripe grapes.